You've probably held one in your hand without realizing how much work these tiny power sources do. Coin cell batteries—those small, round discs that look like little metal coins—power dozens of devices you use every day. From the moment your watch alarm goes off to when you lock your car with a remote, these compact batteries are quietly keeping things running.
We're talking about batteries so small they fit on your fingertip, yet they can power devices for years. At Voniko Batteries, we've seen how these miniature powerhouses have become the go-to solution for everything from your computer's motherboard to your kid's toys. Let's break down where you'll find them and why they work so well.
Watches and Timekeeping Devices

Wristwatches were one of the original homes for coin cell batteries, and they remain one of the most common uses today. Both analog and digital watches rely on these batteries because they draw very little power and need to last for years.
These batteries can typically run a wristwatch for well over a year in continuous use. That's because quartz movements and simple digital displays don't require much energy. You'll find them in everything from basic timepieces to fitness trackers that monitor your daily steps. The CR2032 and similar lithium coin cells deliver the steady 3-volt output these devices need.
Car Key Fobs and Remote Controls
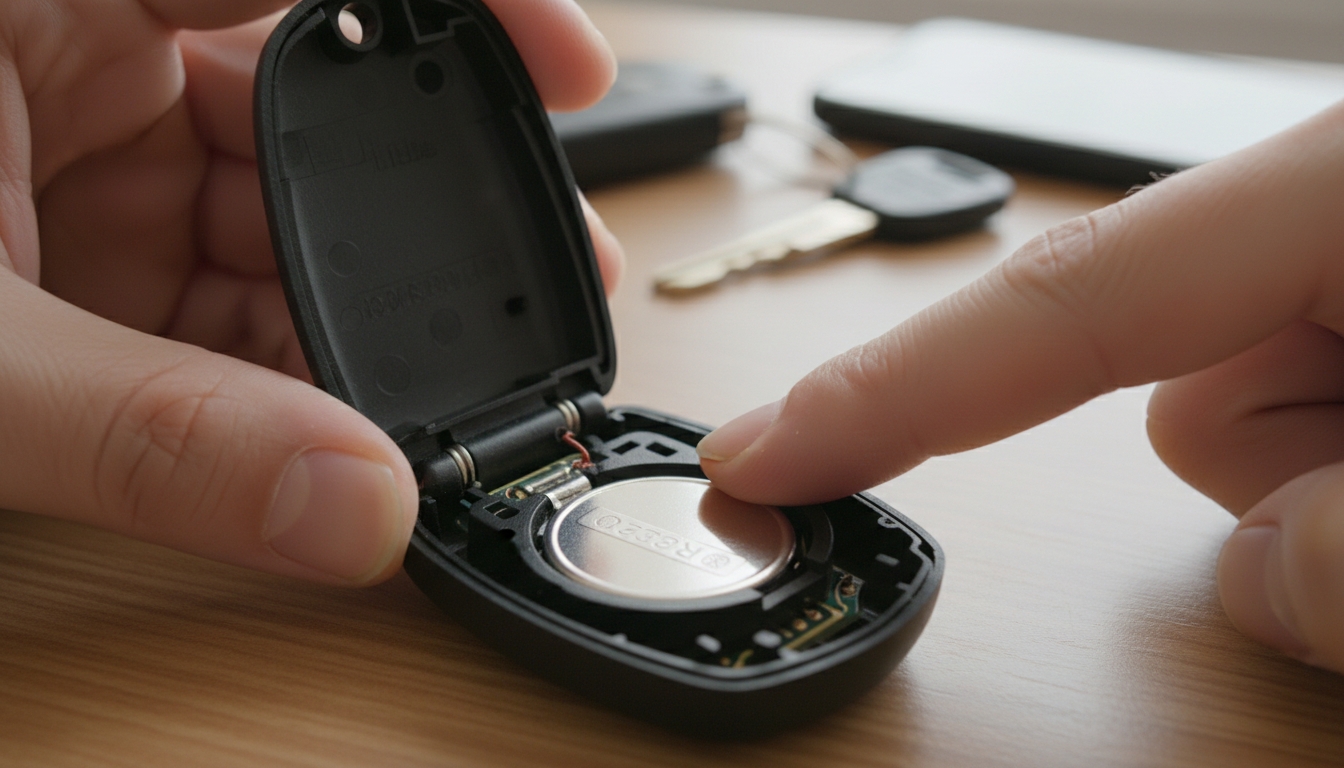

Ever had your car remote die in a parking lot? That's usually a coin cell battery giving up. Remote key fobs are one of the primary applications for these small batteries. They need reliable power that can handle occasional bursts of energy when you press the unlock button.
Car key remotes use coin cells because they offer long service life and can withstand extreme temperatures. Your key fob might sit in freezing weather or baking heat inside your car, and these batteries keep working. TV remotes, garage door openers, and other household remote controls also run on the same technology. Common household items like calculators, thermometers, and car alarm keyfobs rarely need battery replacements.
Computer Motherboards and Memory Backup
Your computer remembers the date and time even when it's unplugged, thanks to a coin cell battery. These batteries provide power to the system clock and CMOS settings while the computer is powered off. Look inside a desktop computer or laptop, and you'll spot a CR2032 sitting on the motherboard.
Button cell batteries provide backup power to maintain BIOS settings and real-time clocks in computer motherboards and other electronic devices. Without this battery, your computer would forget basic settings every time you turned it off. The low power draw means one battery can last 5-7 years or more, depending on how often you use the computer.
Medical Devices and Health Monitors
Medical technology relies heavily on coin cell batteries for portable devices. Glucose meters, hearing aids, and other portable medical tools benefit from the reliability and longevity of these batteries. People managing diabetes test their blood sugar multiple times daily, and they need batteries that won't quit unexpectedly.
Miniature zinc-air batteries are commonly used in hearing aids and medical instruments. Digital thermometers, heart rate monitors, and even some pacemakers use variations of coin cell technology. The stable voltage output and compact size make them perfect for devices that need to be small and dependable.
Toys, Calculators, and Small Electronics
Walk down the toy aisle, and you'll see countless items powered by coin cells. Alkaline batteries in the LR series are widely used for low-drain devices like calculators and toys. Small LED lights, keychain games, and novelty items all run on these batteries because they're cheap and easy to replace.
Many pocket-sized and scientific calculators use button cell batteries to power their electronic components, allowing for portable and long-lasting functionality. The alkaline battery versions provide 1.5 volts and work great for devices that don't need high power. Kids' toys with blinking lights or simple sound effects can run for months or even years on a single battery.
IoT Sensors and Smart Home Devices
The smart home revolution brought new life to coin cell batteries. Internet of Things devices, including smart home gadgets and wireless sensors for temperature, motion, and humidity, use these batteries to provide real-time data for home automation. Doorbell sensors, window alarms, and fitness trackers all depend on compact power sources.
Wearable technology such as fitness trackers and smart rings often includes coin cell batteries because they are lightweight and long-lasting, and some smart tags use this battery to help locate lost items like keys or wallets. These applications need batteries that can sit idle for long periods but spring into action when needed. Our rechargeable options work well for devices that need frequent power cycling.
Why Coin Cell Batteries Work So Well
What makes these batteries so popular across so many applications? Most button cells have low self-discharge, holding their charge for a long time if not used, and common chemistries include zinc, lithium, manganese dioxide, and silver oxide. This means you can buy them in bulk and they'll still work years later.
Alkaline coin cells like the LR44 have a shelf life of 3 years, while lithium coin cells (CR2032, CR2025, CR2016) can be stored for 7 years without significant power loss. Standard alkaline cylindrical batteries (AA, AAA, C, D) offer even longer shelf life of 10 years. The compact design fits into tight spaces where larger batteries won't work. They're also widely available and standardized, so finding replacements is easy. You can learn more about their reliability in our guide on whether lithium coin cell batteries leak.
Conclusion
Coin cell batteries punch way above their weight. These tiny power sources run watches, unlock cars, keep computers running, monitor health, entertain kids, and power smart homes. Their low self-discharge, long shelf life, and compact size make them the perfect solution for low-drain devices that need reliable, long-lasting power. Whether you need lithium coin cells for high-drain devices or alkaline versions for everyday gadgets, understanding what these batteries do helps you pick the right one. Keep a few spares around—you'll be glad you did when your car remote or bathroom scale stops working at the worst possible moment.
FAQs
How long do coin cell batteries typically last in devices?
Lifespan varies by device and usage. In low-drain applications like watches or computer motherboards, a lithium coin cell can last 5-7 years depending on the specific model. Premium lithium batteries like the CR123A can last up to 15 years in storage. Devices with higher power demands or frequent use, like key fobs or fitness trackers, might need replacement every 1-3 years. Temperature extremes and storage conditions also affect longevity.
Can I use rechargeable coin cell batteries in any device?
Not always. Rechargeable coin cells have different voltage outputs and capacity compared to disposable ones. Most standard devices are designed for non-rechargeable batteries. Check your device manual first—using the wrong type can damage electronics or cause poor performance. Rechargeable versions work best in devices specifically designed for them.
What's the difference between CR and LR coin cell batteries?
The prefix tells you the chemistry. CR batteries are lithium-based and provide 3 volts with longer life and better temperature performance, operating from -4°F to 140°F (-20°C to 60°C). LR batteries are alkaline, provide 1.5 volts, and cost less but don't last as long, with an operating range of -0.4°F to 122°F (-18°C to 50°C). You can't swap them—devices are designed for specific voltage requirements.
Are coin cell batteries dangerous if swallowed?
Yes, especially for children. When swallowed, these batteries can cause severe internal burns within hours, even if the battery is dead. Keep them away from kids and pets. If ingestion happens, seek medical help immediately. Store batteries in childproof containers and make sure device battery compartments are secure.
Why do some devices use multiple coin cell batteries?
Some devices stack multiple coin cells to increase voltage or capacity. Two 1.5-volt batteries in series provide 3 volts, while parallel configuration extends runtime. Higher-power devices like certain LED lights or laser pointers need more energy than a single cell can provide. This design keeps devices compact while meeting power needs.




















